Probiotics For UTI: Definition And Best Strains
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary system, such as the bladder, urethra, or kidneys. UTI's are becoming increasingly common globally, with a with a lifetime incidence of 50−60% in adult women according to research by M Medina.
Probiotics, specifically those in the Lactobacillus group, may be beneficial for the treatment and prevention of urinary tract infections. Lactobacilli are believed to dominate the urogenital flora in healthy women and restoring the balance with lactobacilli may offer protection against UTIs according to L Singhal.
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection?
A UTI is an infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. UTIs are commonly caused by bacteria entering the urethra from the skin or rectum and infecting the urinary tract. The most common type of UTI is a bladder infection known as cystitis.
Symptoms of UTIs can include frequent urination, pain or discomfort during urination, changes in urine appearance, lower abdominal pain, fatigue, and sometimes fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and back or side pain. UTIs are a common condition and can be treated with antibiotics.
A urinary tract infection refers to an infection in any part of the urinary system. When hematuria is absent, it means there is no blood in the urine along with the infection. Conversely, UTI with hematuria indicates the presence of blood in the urine alongside the infection.
What Is The Urinary Microbiome?
The urinary microbiome refers to the microbial community present in the urinary tract, specifically in the bladder-obtained urine. It has been discovered that urine in the bladder is not usually sterile, challenging previous beliefs according to a 2019 study authored by K Thomas-White.
The urine microbiome is influenced by various factors such as age, urinary metabolites from diet, personal hygiene, and voiding habits. The microbial composition of the urinary microbiome differs between individuals and can vary between children and adults. Common genera found in the urinary microbiome include Prevotella, Escherichia, Enterococcus, Streptococcus, and Citrobacter according to a 2021 study authored by V Perez-Carrasco.
What Are The Features Of Urinary Microbiome?
The most distinguishing features of the urinary bacterial microbiome are from the Proteobacteria phylum, specifically Enterobacteriaceae and Escherichia according to a 2022 study authored by G Lane.
The diversity of the urinary microbiome varied depending on the type of bladder management used. Patients using indwelling catheters had a higher relative abundance of Pseudomonas, while males had a higher relative abundance of Aerococcus compared to females.
What Is The Best Probiotic For UTI?
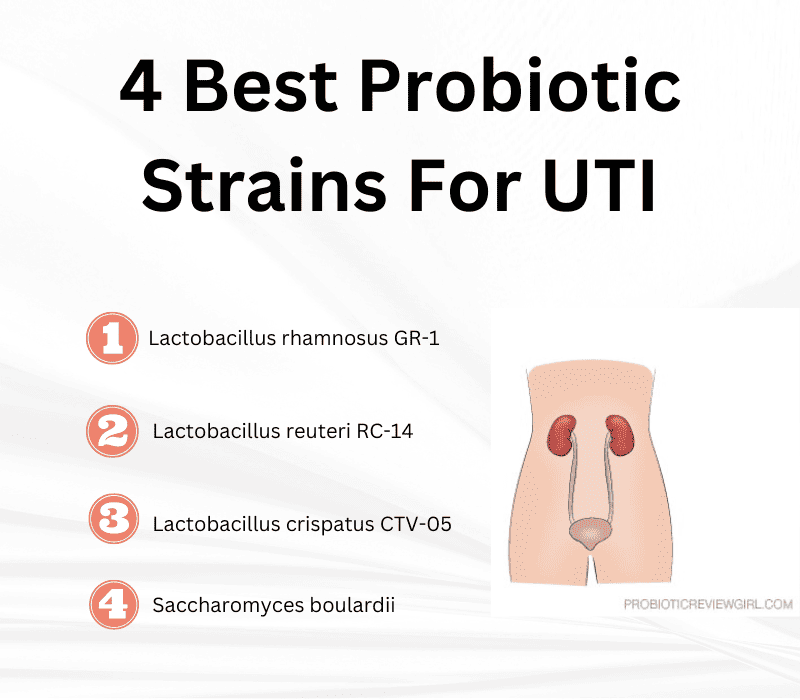
The 4 best probiotics for UTI are Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1®, Lactobacillus reuteri RC-14®, Lactobacillus crispatus CTV-05 and Saccharomyces boulardii as shown in the graphic above. These strains have been reported to support a healthy urinary microbiome and may be beneficial for those experiencing recurrent urinary tract infections.
How Effective Is D-Mannose For UTI?
D-Mannose can be just as effective as antibiotics for Urinary Tract Infections according to research. A 2022 review authored by F Wagenlehner, found that is that d-mannose is a promising alternative to antibiotics for the treatment of acute uncomplicated urinary tract infections in women.
Clinical cure rates and symptom relief were comparable between d-mannose monotherapy and antibiotics, indicating that d-mannose may be a safe and effective option for UTI treatment.
D-Mannose is not a probiotic but a naturally occurring monosaccharide that inhibits bacterial adhesion to urothelial cells. The C Quattrone study previously referenced, showed that you can take probiotics and D-Mannose together.
Can I Take Probiotics With Antibiotics For UTI?
Yes, the use of probiotics with antibiotics is suggested as a complementary approach to antibiotics for UTI prevention as shown previously in the KC Anukam study. Antibiotics are medications that are used to treat bacterial infections by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria.
Antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the urinary tract, altering the composition and diversity of the urinary microbiome and potentially leading to urinary tract infections or other complications.
Can Probiotics Restore Vaginal Flora?
Yes, Probiotics have the potential to restore and rebalance the disrupted urinary microbiome caused by antibiotics. They can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing the risk of urinary tract infections and related complications according to a 2008 study authored by D Borchert.
Can Probiotics Cause UTI?
No, probiotics cannot cause urinary tract infections in humans. There has been previous controversy regarding the use of probiotics for UTIs, but current evidence indicates that the risk of developing a UTI from probiotic use is very low according to a 2018 study authored by T Akgül.
Clinical studies have not reported any serious infections in the general population. However, there are rare cases of UTIs caused by specific strains of Lactobacillus bacteria, although these occurrences are exceedingly uncommon according to a 2022 study authored by F Rossi.
Can Candida Cause Urinary Tract Infection?
Yes, Candida albicans remains the most common cause of urinary tract infection candidiasis. This is the most frequent nosocomial fungal infection worldwide according to a 2015 study authored by P Behzadi.
While there are some variations in the distribution of Candida species causing urinary tract infections in different countries, Candida albicans still ranks as the primary species responsible for these infections. Candida is a type of fungus that can cause infections, particularly in the urinary tract.
Is Kefir Good For Urinary Tract Infection?
Yes, Kefir is good for Urinary Tract Infection according to research. A 2020 study authored by M Ghane, found that certain probiotic strains of Lactobacillus isolated from kefir demonstrated antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli, the bacteria responsible for urinary tract infections.
Kefir is a fermented milk beverage that contains beneficial probiotic bacteria and yeast, known for its potential health benefits.
How To Take Probiotics For UTI's?
To take probiotics for UTI's you should also try to stay hydrated, practice good vaginal hygiene, urinate after sexual activity, consider supplements like D-mannose or cranberry juice, maintain a balanced diet, and prioritize gut health. Take probiotics 30-minutes before any meals to give them the best chance of reaching your intestines.
Dr. Sara Mesilhy has a Master’s degree in Gastroenterology and holds a membership with the Royal College of Physicians of the United Kingdom. She completed her Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) at Cairo University and is currently part of the ProbioticReviewGirl medical team.